
1041) Which of the following statements related to the perioral region is FALSE?
A. The lower third of the face is subdivided into thirds, the upper one third includes the upper lip and the lower two thirds the lower lip and the chin.
B. The oral commisure should be within a vertical line drawn from the medial limbus of the iris
C. The lips may have an inter-labial gap of 3 mm on repose.
D. The lower lip, on profile, is more anteriorly positioned than the upper lip.
E. The white roll of the lip separates the vermillion from the skin.
1042) Which of the following IS a DEEP peeling agent?
A. 10% of trichloroacetic acid (TCA)
B. 20% of trichloroacetic acid (TCA)
C. 35% of trichloroacetic acid (TCA)
D. Jessner's solution
E. Baker-Gordon solution
1043) Which of the following is the appropriate END POINT for medium peeling agents applied to the perioral area?
A. Erythema of the skin
B. White frost of the skin
C. Pink coloration of the dermis
D. Chamois coloration of the dermis
E. Brown coloration of the dermis
1044) The "marionette lines" are produced by the hyperactivity of ONE of the following perioral muscles
A. Orbicularis oris
B. Risorius
C. Depressor anguli oris
D.Depressor labii inferioris
E. Mentalis
1045) Which of the following complications is THE LEAST in frequency to occur using 35% Trichloroacetic acid (TCA) peeling agent?
A. Erythema
B. Hypopigmentation
C. Hyperpigmentation
D. Lines of demarcation between peeled and non peeled areas
E. Scarring
1046) The drawing below represents a plane from the subnasale to the pogonium. Which of the following is the proper position of the lower lip and upper lip in relation to the mentioned plane?
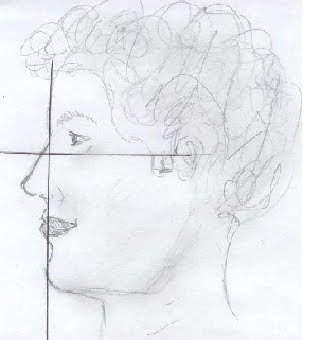
A. At the same plane
B. Upper lip 3.5 mm, lower lip 2.2 mm, both anteriorly
C. Upper lip 2.2 mm, lower lip 3.5 mm, both anteriorly
D. Upper lip 4.5 mm, lower lip 3.5 mm, both anteriorly
E. Upper lip 3.5 mm, lower lip 4.5 mm, both anteriorly
1047) Which of the following is NOT a component of the classic Baker-Gordon peeling solution?
A. 3 ml of phenol 88%
B. 8 drops of Septisol
C. 3 drops of crotton oil
D. 8 ml of lactic acid
E. 2 ml of distilled water
1048) Which of the following lip augmentation materials is a PERMANENT injectable filler?
A. Zyderm
B. Zyplast
C. Restylene
D. Juvederm
E. Artecoll
1049) Which of the following complications is MOST commonly seen in the use of alloplastic mandibular implants?
A. Hematoma
B. Infection
C. Sensory alterations
D. Marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve injury
E. Bony resorption
1050) Which of the following is the MOST commonly used chin implant material?
A. Silicone
B. Proplast
C. Gore-Tex
D. Mersilene
E. Hydroxyapatite
ANSWERS & REFERENCES
1041) D The lower lip, on profile, is more anteriorly positioned than the upper lip.
Perkins S. W., Sandel IV H. D.: Anatomic Considerations, Analysis, and the Aging Process of the Perioral Region, Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America, , (Perkins S. W. , editor), Vol. 15, No. 4, November 2007., pp.403-407
1042) E Baker-Gordon solution
Perkins S. W., Balikian R.: Treatment of Perioral Rhytids, Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America, , (Perkins S. W. , editor), Vol. 15, No. 4, November 2007., pp.409-414
1043) B White frost of the skin
Perkins S. W., Balikian R.: Treatment of Perioral Rhytids, Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America, , (Perkins S. W. , editor), Vol. 15, No. 4, November 2007., pp.409-414
1044) C Depressor anguli oris
Kaplan S. E., Sherris D. A., Gassner H. G., Friedman O.: The Use of Botulinum Toxin A, Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America, , (Perkins S. W. , editor), Vol. 15, No. 4, November 2007., pp.415-421
1045) E Scarring
Perkins N. W., Smith Jr.,S. P., Williams II E. F.:Perioral Rejuvenation: Complementary Techniques and Procedures, Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America, , (Perkins S. W. , editor), Vol. 15, No. 4, November 2007., pp.423-432
1046) B Upper lip 3.5 mm, lower lip 2.2 mm, both anteriorly
Perkins S. W., Sandel IV H. D.: Anatomic Considerations, Analysis, and the Aging Process of the Perioral Region, Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America, , (Perkins S. W. , editor), Vol. 15, No. 4, November 2007., pp.403-407
1047) D 8 ml of lactic acid
Perkins S. W., Balikian R.: Treatment of Perioral Rhytids, Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America, , (Perkins S. W. , editor), Vol. 15, No. 4, November 2007., pp.409-414
1048) E Artecoll
Segall L., Ellis D. A.F: Therapeutic Options for Lip Augmentation, Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America, , (Perkins S. W. , editor), Vol. 15, No. 4, November 2007., pp.485-490
1049) C Sensory alterations
Mittelman H., Spencer J. R., Chrzanowski D. S.: Chin Region: Management of Grooves and Mandibular Hypoplasia with Alloplastic Implants, Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America, (Perkins S. W. , editor), Vol. 15, No. 4, November 2007., pp.445-460
1050) A Silicone
Mittelman H., Spencer J. R., Chrzanowski D. S.: Chin Region: Management of Grooves and Mandibular Hypoplasia with Alloplastic Implants, Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America, (Perkins S. W. , editor), Vol. 15, No. 4, November 2007., pp.445-460
http://www.emedicine.com/plastic/topic56.htm
No comments:
Post a Comment