801-810
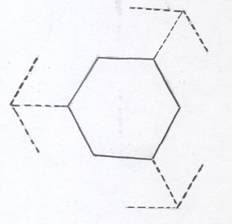
801) Which of the following arteries is the one indicated by the black arrow in the drawing below?
 A. Thoracoacromial Artery
A. Thoracoacromial ArteryB. Lateral Thoracic Artery
C. Transverse Cervical Artery
D. Mammary Artery Perforators
E. Dorsal Scapular Artery
802) Which of the following managements is the IDEAL for treatment of Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans localized in the head and neck area?
A. Currettage followed by electrosurgery
B. Wide surgical excision
C. Mohs surgery
D. Radiation therapy
E. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy
803) In the normal Human Scalp, what is the percentage of Hair Follicules in the TELOGEN PHASE?
A. 1%
B. 5%
C. 10%
D. 20%
E. 30%
804) Which of the following statements about skin graft vascularization is FALSE?
A. Skin grafts initially adhere to the recipient bed by fibrin.
B. Skin grafts receive fluid during the first 48 hours by plasmatic imbibition.
C. Skin grafts will create, after 48 hours, connections between preexisting blood vessels and their bed (inosculation).
D. Skin grafts are firmly attached to their new blood supply by the ninth day.
E. Skin grafts usually attain normal sensory innervation after healing is complete.
805) Which of the following statements regarding normal periocular anatomic relationships is FALSE?
A. Brow at or above Superior Orbital Rim
B. Vertical Palpebral Aperture (10 mm)
C. Horizontal Palpebral Aperture (34 mm)
D. Lateral Canthal Angle (Acute)
E. Lower Lid Margin Below Inferior Limbus
806) Which of the following statements about orbital anatomy is TRUE?
A. The Orbital Walls are formed by 6 bones.
B. The Frontal Bone forms the entire Orbital Roof.
C. The Optic Foramen is located in the Greater Wing of the Sphenoid.
D. The Anterior Ethmoidal Foramina is located 18 mm from the Frontoehtmoidal Suture.
E. The Posterior Ethmoidal Foramina is located 36 mm from the Frontoehtmoidal Suture.
807) Which of the following statements about Eyelid Ptosis evaluation is TRUE?
A. The normal measurement of the Palpebral Fissure is usually less than 10 mm.
B. The normal Eyelid Crease measurement in females is usually less 10 mm.
C. Normal Levator Function is usually greater than 11 mm.
D. Margin Reflex Distance-1 (MRD1) is the distance between the Center of the Pupil in primary position and the Central Margin of the Lower Eyelid.
E. Margin Reflex Distance-2 (MRD2) is the distance between the Center of the Pupil in primary position and the Central Margin of the Upper Eyelid.
808) Which of the following is the BEST management for a Dorsal Nasal Cyst noted one year postrhinoplasty?
A. Conservative and gentle daily massage
B. Needle aspiration
C. Incision and drainage
D. Corticoid injections
E. Surgical excision
809) Which of the following is THE MOST RELIABLE indicator for identifying a patient at risk of developing postblepharoplasty Dry Eye Syndrome?
A. History.
B. Schirmer’s test
C. Tear Film Break-up Time
D. Quantitative Tear Lysozyme Level
E. Corneal Staining with Rose Bengal Solution
810) Which of the following statements about Corneal Abrasion postblepharoplasty is FALSE?
A. A sterile corneal shield coated with a bland ophthalmologic ointment is useful for prevention.
B. A temporary Frost Traction Suture can help to protect the eye during Lower Lid Blepharoplasty.
C. The use of ophthalmologic ointment is helpful to avoid drying and Corneal Ulcer Formation.
D. Rose Bengal Solution staining and the Slit Lamp will made the diagnosis.
E. The treatment of Corneal Abrasion is to close the eye, use antibacterial ointment and patch for 48 hours.
ANSWERS & REFERENCES
801) B Lateral Thoracic Artery
Annino Jr., D. J, Shu R. S: Musculocutaneous Flaps, Chapter 46 in Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (Papel I, editor), second edition, 2002, pp. 560-566
Annino Jr., D. J, Shu R. S: Musculocutaneous Flaps, Chapter 56 in Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (Papel I, editor), Third edition, 2009, pp. 757-764
802) B Wide surgical excision
Hendrix J. D. Jr., Slingluff C. L.: Cutaneous Malignancies Diagnosis and Treatment, Chapter 42 in Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (Papel I, editor), second edition, 2002, pp. 485-507
Hendrix J. D. Jr., Slingluff C. L.: Cutaneous Malignancies Diagnosis and Treatment, Chapter 42 in Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (Papel I, editor), Third edition, 2009, pp. 675-702
803) C 10%
Bennett R.G.: Anatomy anf Physiology of the Skin, Chapter 1, in Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Second Edition, 2002, pp. 10-12
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/835470-overview
804) E Skin grafts usually attain normal sensory innervation after healing is complete.
Angel M.F., Giesswein P., Hawner P.: Skin Grafting, chapter 7 in Operative Plastic Surgery, (Evans G. R.D., editor), McGraw-Hill, 2000, pp.59-65
Triana Jr. R. J., Murakami C. S., Larrabee Jr. W. F.: Skin Grafts and Local Flaps, Chapter 4, Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, (Papel I.D., editor), Second Edition, 2002, pp. 38-54
Hom D. B., Tope W. D.: Minimally Invasive Options and Skin Grafts for Cutaneous Reconstruction, Chapter 53, Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, (Papel I.D., editor), Third Edition, 2009, pp. 703-719
805) E Lower Lid Margin Below Inferior Limbus
Zdinak L. A.: Patient Evalualtion in Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America (Bosniak S. L., editor), Vol. 38, No. 5, October 2005, pp.857-869
Ridley M. B., VanHook S. M.: Aesthetic Facial Proportions, Chapter 11, Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, (Papel I.D., editor), Third Edition, 2009, pp. 119-133
806) E The Posterior Ethmoidal Foramina is located 36 mm from the Frontoehtmoidal Suture.
807) C Normal Levator Function is usually greater than 11 mm.
Edmonson B. C., Wulc A. E.: Ptosis Evaluation and Management in Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America (Bosniak S. L., editor), Vol. 38, No. 5, October 2005, pp.921-946
808) E Surgical excision
Quatela V. C., Russell Ries W.: Aesthetic Facial Surgery, chapter 24 in Complications in Head and Neck Surgery (Krespi and Ossoff, editors), 1993, pp.385-435
809) A History
Quatela V. C., Russell Ries W.: Aesthetic Facial Surgery, chapter 24 in Complications in Head and Neck Surgery (Krespi and Ossoff, editors), 1993, pp.385-435
Gilbard J. P.: The Diagnosis and Management of Dry Eyes, in Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America (Bosniak S. L., editor), Vol. 38, No. 5, October 2005, pp.871-885
810) D Rose Bengal Solution staining and the Slit Lamp will made the diagnosis.
Quatela V. C., Russell Ries W.: Aesthetic Facial Surgery, chapter 24 in Complications in Head and Neck Surgery (Krespi and Ossoff, editors), 1993, pp.385-435
---------------------------------------
Updated: June 25, 2017